If you’re a fan of Netflix’s hit series Stranger Things, you probably already know Natalia Dyer. But even beyond her role as Nancy Wheeler, Dyer has carved a niche for herself as one of Hollywood’s most talented young actresses. Here’s a closer look at her life, career, and what makes her stand out in the entertainment industry.
Early Life and Background
Natalia Dyer was born on January 13, 1995, in Nashville, Tennessee. Growing up in a supportive family, she developed a love for acting at a young age. Dyer attended the Nashville School of the Arts, where she honed her craft, eventually deciding to pursue acting professionally.
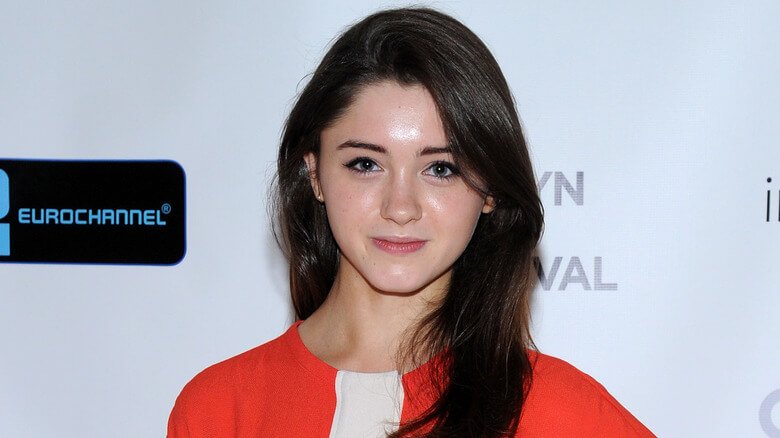

Her Southern roots have remained a part of her charm, giving her a down-to-earth presence that resonates with fans both on and off screen.
Career Beginnings
Dyer began acting in the mid-2000s, landing minor roles in television and independent films. Her first notable appearances were in small projects that showcased her talent but didn’t immediately catapult her to fame. She also appeared in films like Hannah Montana: The Movie (2009), where she played a small but memorable role.
However, it was her role in Netflix’s Stranger Things that became her breakthrough.
Rise to Fame: Stranger Things
In 2016, Natalia Dyer was cast as Nancy Wheeler in Stranger Things, the Netflix sci-fi thriller set in the 1980s. Her portrayal of Nancy—a brave, intelligent, and resourceful teenager—earned critical acclaim.
Over the show’s multiple seasons, Dyer’s character evolved from a high school student struggling with social pressures into a determined young woman taking on dangerous supernatural forces. Fans appreciated her nuanced performance, which balanced vulnerability, strength, and intelligence.
Other Notable Projects
While Stranger Things remains her most recognized role, Dyer has also worked in other films, including:
- Yes, God, Yes (2019): A coming-of-age comedy-drama where she received praise for her performance.
- Velvet Buzzsaw (2019): A satirical horror-thriller in which she starred alongside Jake Gyllenhaal.
- I’m Your Woman (2020): A crime drama that showcased her ability to take on more mature and complex roles.
Her versatility as an actress proves that she’s not just a TV star but a rising talent capable of handling diverse genres.
Personal Life
Natalia Dyer is known for keeping her personal life relatively private, but she has occasionally shared glimpses of her life with fans. She has been in a relationship with her Stranger Things co-star Charlie Heaton, who plays Jonathan Byers, sparking curiosity and admiration among fans.
Outside of acting, Dyer enjoys traveling, fashion, and music, often using her platform to support creative and social causes.
Why Fans Love Her
Fans appreciate Natalia Dyer not just for her talent but also for her authenticity. Her ability to portray complex emotions, combined with her grounded personality off-screen, makes her relatable and inspiring to many young viewers.
Conclusion
From her beginnings in Nashville to starring in one of Netflix’s biggest hits, Natalia Dyer has proven herself as a versatile and talented actress. With her career still on the rise, fans can look forward to seeing her take on even more challenging and exciting roles in the future.
Whether you know her as Nancy Wheeler or are just discovering her work, Natalia Dyer is a name worth remembering in Hollywood.
(FAQs) About Natalia Dyer
1. Who is Natalia Dyer?
Natalia Dyer is an American actress best known for playing Nancy Wheeler in Netflix’s hit series Stranger Things.
2. How old is Natalia Dyer?
She was born on January 13, 1995, which makes her 31 years old as of 2026.
3. Where is Natalia Dyer from?
Natalia Dyer is from Nashville, Tennessee, United States.
Also Read: iPledge Login: A Complete Guide
4. What is Natalia Dyer famous for?
She is most famous for her role as Nancy Wheeler in Stranger Things, a sci-fi horror series that became a global success.
5. When did Natalia Dyer start acting?
Natalia began acting as a child in community theater. Her film debut was in Hannah Montana: The Movie (2009).
6. Is Natalia Dyer dating anyone?
Yes, she has been in a long-term relationship with her Stranger Things co-star Charlie Heaton, who plays Jonathan Byers.
7. What other movies and TV shows has Natalia Dyer appeared in?
Some of her notable projects include:
- Velvet Buzzsaw (2019)
- Things Heard & Seen (2021)
- Based on a True Story (2023)
- I Believe in Unicorns (2014)
8. Did Natalia Dyer win any awards?
She won a Screen Actors Guild (SAG) Award as part of the Stranger Things ensemble cast.
9. Where did Natalia Dyer study?
She attended the Nashville School of the Arts and later studied at New York University (NYU).
10. What is Natalia Dyer doing now?
Following the success of Stranger Things, Natalia continues to work on film and television projects, focusing on diverse and character-driven roles.